What Are the Early Warning Signs of Brain Tumors?



What Are the Warning Signs of Brain Tumors?
Early warning signs for brain tumors can depend on your brain tumor:
- Type
- Location
- Size
When brain tumors are small, you might not have any symptoms. But that can change if your tumor grows.
What Are Benign Primary Brain Tumors?
Noncancerous tumors start in your brain, also called benign primary brain tumors. Benign means the tumor isn't cancer, so doesn't spread. You're more likely to get a primary benign brain tumor if you are:
- An adult. About 82% of benign tumors happen in adults.
- An older adult. Your chances get higher as you get older.
- A woman: Women have a higher risk than men.

Warning Signs: Headaches and Seizures
You can get a headache from everyday causes like stress, lack of sleep, or certain foods. But headaches as an early symptom of brain tumors will often:
- Be more intense than a normal headache
- Be worse in the morning
- Not go away after you take over-the-counter painkillers
- Also come with feeling dazed, or having trouble speaking or walking

Warning Signs: Nausea and Vomiting
Feeling nauseated and vomiting are very common and can happen for many reasons. But a brain tumor takes up more room inside your skull and presses on your brain. The pressure can lead to nausea and vomiting. Take notes and write down if your nausea and vomiting:
- Last more than a couple of days
- Get worse in the mornings
- Get worse when you are lying down

Warning Signs: Vision Problems
With dry eyes, headaches, or eye disease, you can often get vision trouble. But a brain tumor can put pressure on your brain stem and optic nerve (connects your eye and brain). This can impact your vision and cause:
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Vision loss, for a few seconds after lying down or standing up
- Blind spots, where you lose part of your field of vision
Warning Sign: Hearing Problems
An ear infection or getting older can cause hearing problems, but rarely it's an acoustic neuroma. That's a benign brain tumor that grows on the nerve connecting the inner ear to your brain.
Your inner ear controls hearing and balance, so the tumor can cause:
- Tinnitus, ringing in your ears
- Gradual hearing loss, sometimes in one ear
- Balance problems
- Hearing changes
Mild symptoms often come on slowly before you're aware of hearing changes.

Warning Sign: Numbness or Tingling
You might get numb or tingle because you've been in the same position for a long time. Or maybe it's from a migraine, infection, or carpal tunnel syndrome. But if your brain tumor blocks your brain signals to your body, you can get tingling and numbness in your:
- Face
- Arms
- Hands
- Legs
- Feet

Warning Sign: Loss of Balance and Coordination
If you feel dizzy, you may have an ear infection or be dehydrated (didn't get enough water). Rarely, a brain tumor can press near the back of your brain in an area called the cerebellum and cause problems with your:
- Balance (dizziness)
- Coordination
- Movement
- Walking
A tumor in the front part of your brain (frontal lobe) can also change how you think, balance, and walk --- you're at higher risk for falls.

Warning Sign: Changes in Personality or Behavior
Your brain controls your personality, so a tumor could change how you act and feel. Swelling, pressure on your brain and nerves, and medications can cause symptoms such as being:
- More cranky
- Anxious
- Confused
- Depressed
- Moody
- Not as interested in the things you used to enjoy
- More aggressive
- Forgetful

Warning Sign: Cognitive Problems
Cognitive problems can depend on where your tumor sits on your brain, the size, and your brain tumor treatment. Your brain tumor can cause trouble with how you think, reason, learn, and concentrate. If your brain tumor causes cognitive problems, you might notice:
- Memory loss
- A harder time making decisions
- Plans being harder to make
- Trouble solving problems

Warning Sign: Speech and Language Problems
A frontal or temporal lobe (behind your ears) tumor can impact your speach and language. The frontal lobe controls speech, but the temporal lobe helps you know what you're hearing. If your tumor presses on the part of the brain that controls speech, you might have:
- Trouble speaking
- A hard time finding the right words
- Slurred words
- A slower speaking speed
- Strained speech
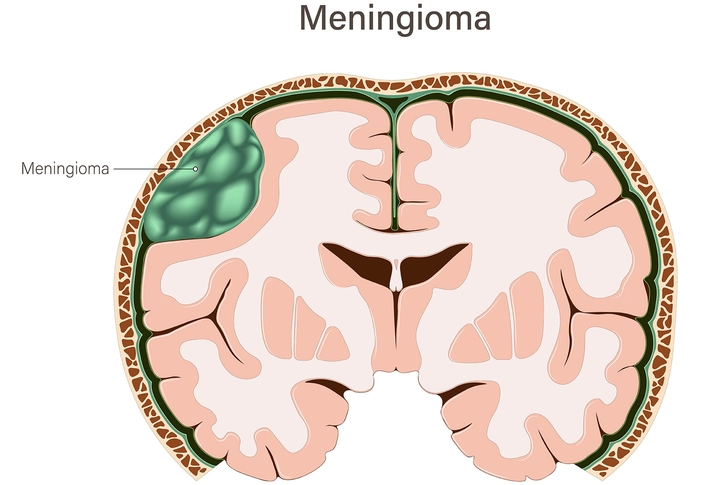
Warning Signs of Meningioma
Meningiomas are mostly benign, slow-growing tumors that form in the membranes around your brain and spinal cord. About one-third of all primary brain tumors are meningiomas, and symptoms can include:
- Headaches
- Vision changes
- Hearing problems
- Seizures
- Weakness in your arms or legs
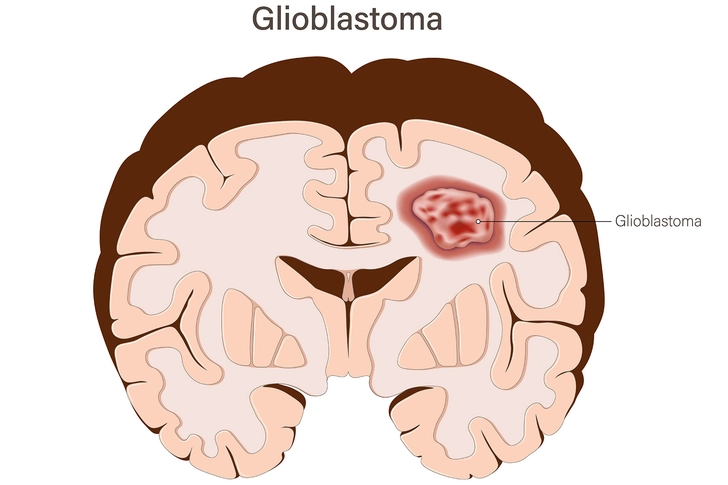
Warning Signs of Glioblastoma
Glioblastomas are quickly growing cancerous tumors that are classified as grade 4. That means the tumors can spread quickly and you may get:
- Intense headaches
- Nausea
- Vision problems
- Trouble speaking
- Thinking problems
- Problems understanding
- Memory issues
- Personality changes
- Seizures
Warning Signs of Astrocytoma
Astrocytomas are tumors that grow from a star-shaped cell called an astrocyte in your brain or spinal cord. These noncancerous tumors can grow slowly to very aggressively. With an astrocytoma, you may get:
- Headaches
- Speech problems
- Memory loss
- Personality changes
- Seizures
Warning Signs of Craniopharyngioma
Craniopharyngiomas are rare noncancerous brain tumors that grow near your pituitary gland --- a pea-sized gland at the base of your brain that makes hormones to control many body functions. More common in children and older adults, craniopharyngiomas that press on the pituitary gland can cause:
- Slowed growth
- Delayed development
Vision problems can also happen if the tumor presses on your optic nerve.

When to Talk to a Doctor
Many brain tumor early warning signs can have everyday causes. But it's always a good idea to talk to your doctor if your symptoms are new, unusual, serious, come on suddenly, don't go away, or get worse. See your doctor if you get:
- Serious headaches
- Seizures
- Sudden weakness or numbness
- Speech, vision, or hearing problems
- Personality or behavior changes
- Trouble thinking
- Balance problems
- Serious nausea or vomiting
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
- E+/Getty Images
- Science Photo Library/Getty Images
- Moment/Getty Images
- iStock/Getty Images
- Westend61/Getty images
- E+/Getty Images
- iStock/Getty Images
- Jupiterimages/Getty Images
- DigitalVision/Getty Images
- iStock/Getty Images
- E+/Getty Images
- iStock/Getty Images
- iStock/Getty Images
- Science Photo Library/Getty Images
- Science Photo Library/Getty Images
- E+/Getty Images
SOURCES:
Mayo Clinic: "Brain tumor," "Acoustic neuroma," "Meningioma," "Glioblastoma," "Astrocytoma," "Craniopharyngioma."
National Brain Tumor Society: "Signs & Symptoms," "Improving Balance and Preventing Falls for Patients with Brain Tumors," "How to Help Patients with Brain Tumors Navigate Speech and Language Challenges."
Brain Tumor Network: "Signs & Symptoms of a Brain Tumor."
Johns Hopkins Medicine: "Brain Tumor Types," "Brain Tumors and Brain Cancer."
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center: "Types of Primary Brain Tumors," "When Is a Headache a Symptom of a Brain Tumor? Very Rarely."
Moffitt Cancer Center: "Are Nausea and Vomiting Symptoms of a Brain Tumor?" "Can Brain Tumors Affect Your Vision?" "Do Brain Tumors Cause Numbness and Tingling?" "Can Brain Tumors Cause Mood Changes?"
The Brain Tumour Charity: "Change in vision," "Brain tumour personality changes," "Cognition and learning difficulties because of a brain tumour," "Speech and language difficulties," "Glioblastoma."
Harvard Health Publishing: "Acoustic neuroma: A slow-growing tumor that requires specialized care."
Hackensack Meridian Health: "7 Warning Signs of a Brain Tumor."
University of Rochester Medical Center: "Brain Tumors: Coping with Thinking and Memory Problems."
Jefferson Health: "Understanding Benign Brain Tumors: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment."
Cleveland Clinic: "Astrocytoma."
American Association of Neurological Surgeons: "Astrocytoma Tumors."
Weill Corner Medicine Neurological Surgery: "Symptoms of a Craniopharyngioma."
MedStar Health: "Brain Tumor Signs: When to See a Doctor."
MD Anderson Cancer Center: " 'How I knew I had a brain tumor': 4 survivors share their symptoms."
Oregon Health & Science University Brain Institute: "Brain Tumor Symptoms and Diagnosis."